Home > Know Sundarban >Sundarban Biosphere































Sundarban Biosphere
As part of the Man and Biosphere Programme (MAB), accepted in the general conference of the UNESCO in 1970, the Ministry of Environment & Forests, Govt. of India adopted the National MAB programme and declared the entire 9630 sq. km. Of Sundarban as the Sundarban Biosphere Reserve in 1989 through a notification to establish a formal mechanism for coordinating and integrating diverse activities of conservation, research and training for creating a better situation of harmony between man and environment. The Sundarbans, due to its unique ecosystem, has also been declared as a World Heritage site in 1989. Sundarban Biosphere Reserve has also been included as the second Biosphere Reserve from India , other than Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, in the global network of Biosphere Reserves, in November 2001.
Sundarban, the largest delta in the world, consists of 10,200 sq km of Mangrove Forest , spread over India (4200 sq km of Reserved Forest) and Bangladesh (6000 sq km approx of Reserved Forest) and is also the largest Mangrove Forest in the world. Another 5400 sq km of non-forest, inhabited region in India , along the north and north-western fringe of mangrove forest, is also known as Sundarban region in India . Hence, the total area of Sundarban region in India is 9600 sq km which constitutes the Sundarban Biosphere Reserve. Indian Sundarban is bound on the west by river Muriganga and on the east by rivers Harinbhanga and Raimangal. Other major rivers flowing through this eco-system are Saptomukhi, Thakuran, Matla and Goasaba.
Uniqueness of Sundarban Forest
Sundarban Biosphere Reserve was constituted by Government of India (GOI) in 1989 and it received the recognition of UNESCO under its Man and Biosphere (MAB) Programme in November, 2001. Sundarban National Park , forming the core area of Sundarban Tiger Reserve, received recognition as World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1987. It has been nominated by GOI for recognition as Ramsar Site (a wetland of international importance). Sundarban Tiger Reserve was constituted by GOI under Project Tiger scheme, in 1973. Sundarban is the only mangrove forest in the world which is the home of Tiger. Sundarban Tiger Reserve has the highest tiger population in the world.
Importance of Sundarban Ecosystem
Sundarban has extremely rich diversity of aquatic and terrestrial flora and fauna. Sundarban's highly productive ecosystem acts as a natural fish nursery. Sundarban Mangrove reduces the fury of cyclonic storm and prevents erosion due to tidal action. Finally, millions of people depend on Sundarban Ecosystem for their livelihood and sustenance through fishing, collection of honey and fuelwood/timber.
Topography and Soil
Geologically, the Sundarban delta is the largest prograding delta on the globe. The region is covered solely by quaternary sediments carried and deposited by the rivers Ganges , Matla & Bidyadhari.
Climate and Rainfall
Although the region is situated south of the Tropic of Cancer, the temperature is equable due to its proximity to the sea. Average annual maximum temperature is around 35°C . Average annual rainfall is 1920 mm. Average humidity is about 82% which is more or less uniform throughout the year.
Present status of Faunal Resources
Sundarban mangrove forest is the single largest home of the Royal Bengal Tiger (Panthera tigris). Sundarban is also the only mangrove forest in the world having the tiger as its indigenous population. As per 2004 census, the tiger population in Indian Sundarban is around 274, out of which Sundarban Tiger Reserve and South 24-Parganas Forest Division have 249 Tigers and 25 tigers respectively. There are 58 species of mammals, 55 species of reptiles and around 248 bird species.
Sundarbans also harbors a good number of rare and globally threatened animals including Estuarine Crocodile (Crocodilus porosus), Fishing Cat (Felis viverrina), Common otter (Lutra lutra), Water Monitor lizard (Varanus salvator), Gangetic Dolphin (Platinista gangetica), Snubfin dolphin (Orcella brevirostris), River Terrapin (Batagur baska), marine turtles like Olive Ridley (Lepidochelys olivacea), Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas ), Hawksbill Turtle (Eritmochelys imbricata). Six species of Shark and Ray, which are found here, are included in Schedule I of Wildlife (Protection) Act. These indicate that Sundarban Reserved Forest is a natural biodiversity hot spot.
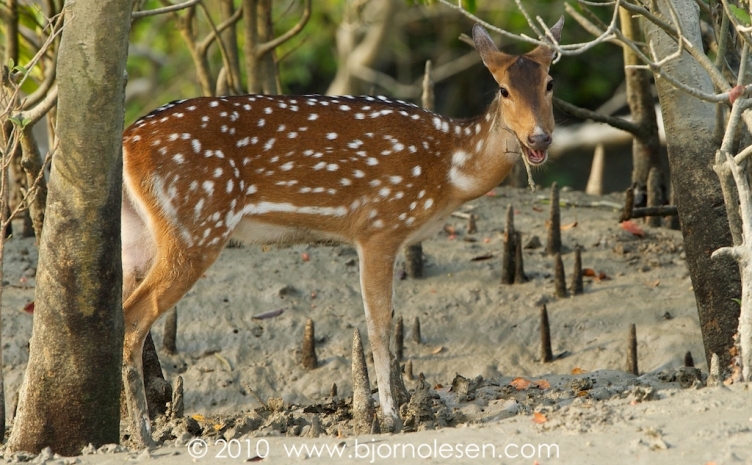
Other mammals comprise of Wild boars, Spotted deer, Porcupines and Rhesus macaque. Among the reptiles, the King cobra, the common cobra, Banded krait, Russells Viper comprise the community of venomous reptiles, while the Python, Checkered Kill-Back, Dhaman , Green Whip Snake and several other species constitute the non-venomous snakes.
Common Plants of Sundarban
| Sl No. | Scientific Name | Local Name | Family |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Acanthus ilicifolius L. (ME) | Harguza | Acanthaceae (S) |
| 2 | A. volubilis wall (ME) | Lata harguza | Acanthaceae (C) |
| 3 | Aegialitis rotundifolia Roxb. (ME) | Tora | Plurnbagenaceae (S) |
| 4 | Aegiceras carnikulatum (L) Blanco (ME) | Khalsi | Myrsinaceae (T) |
| 5 | Avicennia alba Blume (ME) | Piara baen | Verbenaceae (T) |
| 6 | A. marina (Forsk) Vierh. (ME) | Kala baen | Verbenaceae (T) |
| 7 | A. officinalis L. (ME) | Jat baen | Verbenaceae (T) |
| 8 | Aglaia cuculata (Roxb.) Pellegrin | Amur | Meliaceae (T) |
| 9 | Acrostichum aureum L. | Hodo | Ptcridaceae (S) |
| 10 | Bruguiera cyhndrica (L) Blume (ME) | Bakul | Rhizophoraceae(T) |
| 11 | B. gymnorhiza (L) Lam. (ME) | Kankra | Rhizophoraceae(T) |
| 12 | B. Sexangula (Lour) Poirot. (ME) | Kankra | Rhizophoraceae(T) |
| 13 | B. Parviflora (Roxb.) Wight and Arm (ME) | Bakul | Rhizophoraceae(T) |
| 14 | Brownlowia terra (L) Koster | Lata-sundari | Tiliaceac (S) |
| 15 | Cerbera manghas Geartn. | Dakor | Appocynaceae (T) |
| 16 | Clerodendrum inerme (L) Geartn. | Bajai | Verbenaceae (S) |
| 17 | Caesalpinia bunducella (L) Roxb. | Nate | Leguminoseae (S) |
| 18 | C. cristata (L) | Nate | Leguminoseae (S) |
| 19 | Ceriops decandra (Gritt) Ding Hou. (ME) | Jhamti or jele goran | Rhizophoraceae (S) |
| 20 | C. Tagal (Perrottet) C. S. Robinson (ME) | Math goran | Rhizophoraceae (S) |
| 21 | Cynometra iripa Kostel | Singra | Leguminoseae (T) |
| 22 | Derris scandens (Roxb.) Benth. | Kalilata | Leguminoseae (C) |
| 23 | D. heterophylla (WiIld.) Back and Bakh. | Kalilata | Leguminoseae (C) |
| 24 | Dalbergia spinosa Roxb. | ---------- | Leguminoseae (C) |
| 25 | Entada scandens Benth. | Gila | Leguminoseae (C) |
| 26 | Excoecaria agollocha L. (ME) | Genwa | Euphorbiaceae (M) |
| 27 | Finlaysonia obovata L | Dudhilata | Asclapiadeceae (C) |
| 28 | Fimbristylis ferruginea | ---------- | Cyperaccae (H) |
| 29 | Hemithrea compressus L. | ---------- | Graminae (Gr.) |
| 30 | Heliotropium curassavieum Linn. | ---------- | Chenopodiaceae (H) |
| 31 | Heritierafomes Buch-Ham. (ME) | Sundari | Sterculiaceae (T) |
| 32 | Hibiscus tilliaceous L. | Bhola | Malvaccae (T) |
| 33 | Kandelia candel (L) Druce (ME) | Garia | Rhizophoraceae (T) |
| 34 | Lumnitzera racemosa Willd (ME) | Kripa | Combrataceae (T) |
| 35 | Mukuna gigancea (Willd.) D. C. | ---------- | Cucorbitaceae (C) |
| 36 | Myriostachya wightiana (Nessex Steud) Hook f. | Ghash | Graminae (Gr.) |
| 37 | Nypa fruiticans Wurmb (ME) | Golpata | Palmac (T) |
| 38 | Phoenix paludosa Roxb. (ME) | Hental | Palmac (T) |
| 39 | Porterasia coarctata (Roxb.) Tateoca.(ME) | Dhanighash | Pocceae (Gr.) |
| 40 | Pandanus tectorius soland | Keya | Pandanaceae (T) |
| 41 | Pluchea indica Linn. | ---------- | ---------- |
| 42 | RhizopNora apiculata Blume (ME) | Garjan | Rhizophoraceae (T) |
| 43 | R. mucronata Lam. (ME) | Garjan | Rhizophoraceae (T) |
| 44 | Sacharum cylindricum L | Ulu | Graminae (GI.) |
| 45 | Suaeda nudiflora Mog. | Gira sak | Chenopodiaceae (H) |
| 46 | S. monoeca L. | Nonaguru | Chenopodiaceae (H) |
| 47 | S. meritima Dumort. | Nonaguri | Chenopodiaceae (H) |
| 48 | Sesuvium Portulicastrum L. | Jadu Palang | Ficoidae (H) |
| 49 | Salicornea brachiata Roxb. | ---------- | Chenopodiaceae (H) |
| 50 | Salacia prinoides (Willd.) D. C. | ---------- | Celastraceae |
| 51 | Scirpus littorea Schrad | ---------- | Cyperaceae (H) |
| 52 | Sonneratia apetala Buch-Ham. (ME) | Keora | Lythraceae (T) |
| 53 | S. Caseolaris (L) Engl. (ME) | Ora | Lythraceae (T) |
| 54 | S. griffithii Kurz. (ME) | Ora | Lythraceae (T) |
| 55 | S. alba J. Smith (ME) | Ora | Lythraceae (T) |
| 56 | Stenochlaena palustre Bold. | ---------- | ---------- |
| 57 | Stichtocardia tilifolia Hallier F. | ---------- | Manispermaceac (C) |
| 58 | Thespesia populnoides (Roxb.) Kostel. | Paras | Malvaceae (T) |
| 59 | T. populnea (Linn.) Solex Carrea | Paras | Malvaceae (T) |
| 60 | Tamarix troupii Hole | Nona Jhau | Tamaricaceae (T) |
| 61 | T. dioica Roxb. | Nona Jhau | Tamaricaceae (T) |
| 62 | Viscum orientale Van. | ---------- | Loranthaceae (C) |
| 63 | Xylocarpus granatum Koenig. (ME) | Dhundul | Meliaceae (T) |
| 64 | X. mekongensis Pierre (Sym. X. Gangeticus Parkinson) (ME) | Passur | Meliaceae (T) |
Common Birds of Sundarban
| Sl No. | Scientific Name | English/Local Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Phalocrocorax niger | Little cormorant |
| 2 | Ardea purpurea | Purple heron |
| 3 | Butorides striatus | Little green bittern |
| 4 | Ardeola grayii | Pond heron |
| 5 | Bubutcus ibis | Cattle egret |
| 6 | Egretta alba | Large egret |
| 7 | Egretta intermedia | Median egret |
| 8 | Egretta garzetta | Little egret |
| 9 | Nycticorax nycticorax | Hight heron |
| 10 | Anastomus oscitans | Open bill stork |
| 11 | Leptoptilos javanicus | Smaller adjutant stork |
| 12 | Haliastur indus | Brahminy kite |
| 13 | Vanellus indicus | Redwattled lapwing |
| 14 | Numenius phacopus | Whimbrel |
| 15 | *Limosa limosa | Blacktailed godwit |
| 16 | * Tringa hypoleucos | Common sandpiper |
| 17 | * Streptopelia decaocto | Ring dove |
| 18 | Streptopelia chinensis | Spotted dove |
| 19 | Psittacula krameri | Roseringed parakeet |
| 20 | Centropus sinensis | Crow pheasant |
| 21 | Cypsiur parvus | Palmswift |
| 22 | Ceryle rudis | Pied kingfisher |
| 23 | Halcyon orientalis | White-collared kingfisher |
| 24 | Dinopium benghalense | Golden-backed woodpecker |
| 25 | Picoides macei | Fulvus-brested pied woodpecker |
| 26 | Hirundo rustica | Common swallow |
| 27 | * Mirops orientalis | Small green bee-eater |
| 28 | Dicrurus aeneus | Bronzed drongo |
| 29 | Artamus fuscus | Ashy swallow-shrike |
| 30 | Sturnus contra | Pied myna |
| 31 | Acridotheres fuscus | jungle myna |
| 32 | Corvus macrorhynchos | Jungle crow |
| 33 | Coracina melanoptera | Black-headed cuckoo-shrike |
| 34 | Coracina novaehallandiae | Large cuckoo-shrike |
| 35 | Aegithina tiphia | Common iora |
| 36 | Pycnonotus cafer | Redvented bulbul |
| 37 | Rhipidura albicollis | Whitespotted fantail flycatcher |
| 38 | Orthotomus sutorius | Tailor bird |
| 39 | Capsychus saularits | Magpie robin |
| 40 | Nectarinia asiatica | Purple sunbird |
| 41 | Zosterops paipebrosa | White-eye |
| 42 | Passer domesticus | House sparrow |
| 43 | Lonchura malacca | Black-headed munia |
| * marked birds are migratory, others are local | ||
Common Animals of Sundarban
| Sl No. | Scientific Name | English/Local Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Panthera Tigris | Tiger |
| 2 | Felis viverina | Fishing cat |
| 3 | Felis chaus | Jungle cat |
| 4 | Viverra zibatha | Civet cat |
| 5 | Viverricula indica | Small Indian civet |
| 6 | Cervus axis | Axis deer or chital |
| 7 | Sus scrofa | Wild boar |
| 8 | Macaca mulatta | Rhesus monkey |
| 9 | Varanus salvator | Water monitor or salvator lizard |
| 10 | Varanus flaviscense | Yellow monitor or monitor lizard |
| 11 | Crocodilus porosus | Estuarine crocodile |
| 12 | Platanista gangetica | Gangetic dolphin |
| 13 | Chilleseyilum griseum | Tiger shark |
| 14 | Stegestoma fasciatusu | Tiger shark |
| 15 | Ophiophagus hannah | King cobra |
| 16 | Naja naja | Indian cobra |
| 17 | Bungurus fasciatus | Banded krait |
| 18 | Vipera russelli | Russell's viper |
| 19 | Praescutata viperina | Sea-snake |
| 20 | Enhylrina schistosa | Sea-snake |
| 21 | Hydrophis obscurus | Sea-snake |
| 22 | Carcinoscorpius rotundicallada | Horse-shoe crab |
| 23 | Batagur baska | Common batagur |
| 24 | Lepidochelys olivacea | Ridley turtle |
| 25 | Eretmochelys imbrieata | Hawksbill turtle |
| 26 | Lissemys punctata | Pond turtle |
| 27 | Hilsa ilisha | Hilsa |
| 28 | Hilsa toli | Hilsa |
| 29 | Lates calcarifer | Bhekti |
| 30 | Liza tada | Kalagachhi bhangan |
| 31 | Liza microlepis | Ram parse |
| 32 | Mugil oephalus | Aadh bhangan |
| 33 | Liza parsia | Parse |
| 34 | Penaeus monodon | Prawn |
| 35 | Boleophthalmus boddarti | Menomachh |
| 36 | Scylla serrate | Red crab |
| 37 | Coenobita cavipes | Hermit crab |
| 38 | Diogenes avarus | Hermit crab |
| 39 | Clibararius padaversis | Hermit crab |
| 40 | Metaplax crenulata | Metaplax crab |
| 41 | Metaplax dentipes | Metaplax crab |
| 42 | Metaplax distincta | Metaplax crab |
| 43 | Uca Acutus | Fiddler crab |
| 44 | Uca lactea | Fiddler crab |
| 45 | Uca dussumierf | Fiddler crab |
| 46 | Uca triangularis | Fiddler crab |
| 47 | Sesarma bidens | Tree-climbing crab |
| 48 | Sesarma impressa | Tree-climbing crab |
| 49 | Sesarma tacniolatum | Tree-climbing crab |
| 50 | Sesarma tetragonum | Tree-climbing crab |